Redis Cache Monitor Configuration Guide on the Elven Platform
The Redis Cache Monitor from the Elven Platform enables checks based on key queries in Redis. This feature helps configure continuous checks, set alerts, and define thresholds for automatic incident creation, ensuring you are quickly informed of any irregularities in connectivity or service performance.
Redis is an open-source in-memory data store, widely used as a database, cache, and message broker. It supports an advanced data structure model, allowing storage in formats such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, and more, making it highly versatile. With extremely fast response times, Redis is ideal for web applications, gaming, real-time analytics, and messaging systems that require low latency and high performance.
Accessing Redis Cache Monitoring
Navigate to the main menu and click on Services Hub.
In Cache, select the Redis item.
Monitor Configuration
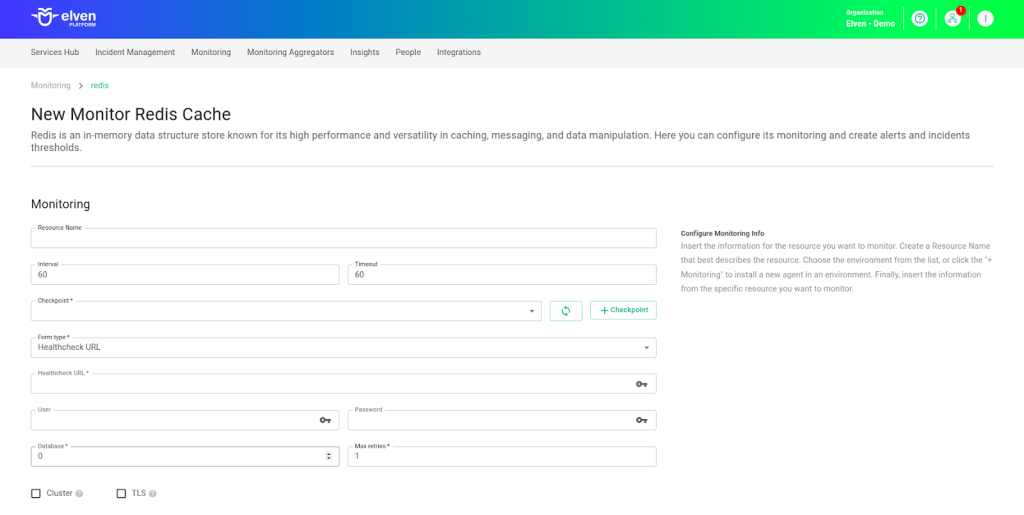
Monitoring the availability of your services has never been easier. Start by giving a clear name to the resource you want to monitor (Resource Name) to make it easier to identify. Then, adjust the Interval between checks and the Timeout for responses.
Select where the monitoring agent is located (Checkpoint Cloud) by choosing the appropriate Environment. If it doesn’t exist, you can create one using + Checkpoint. After this setup, in Form Type, you can choose between User and Password or Healthcheck URL.
In User and Password, you must provide the server address in the Host field and the Port. In Healthcheck URL, simply enter the URL of the resource to be monitored.
Keep in mind that the Host and Healthcheck URL fields only accept URLs. If you need to use an IP address, it must be stored in a Secret to ensure security and organization of sensitive information.
Next, define the Redis database you want to monitor in the Database field, using the corresponding number (e.g., 0 for the default database). Then, set the Max retries value to define the maximum number of reconnection attempts in case of failure, ensuring greater resilience during monitoring.
If Redis is configured as a cluster, enable the Cluster option so that monitoring takes the distributed structure into account. If communication with Redis is done through secure connections, activate the TLS option to use encryption and protect the transmitted data.
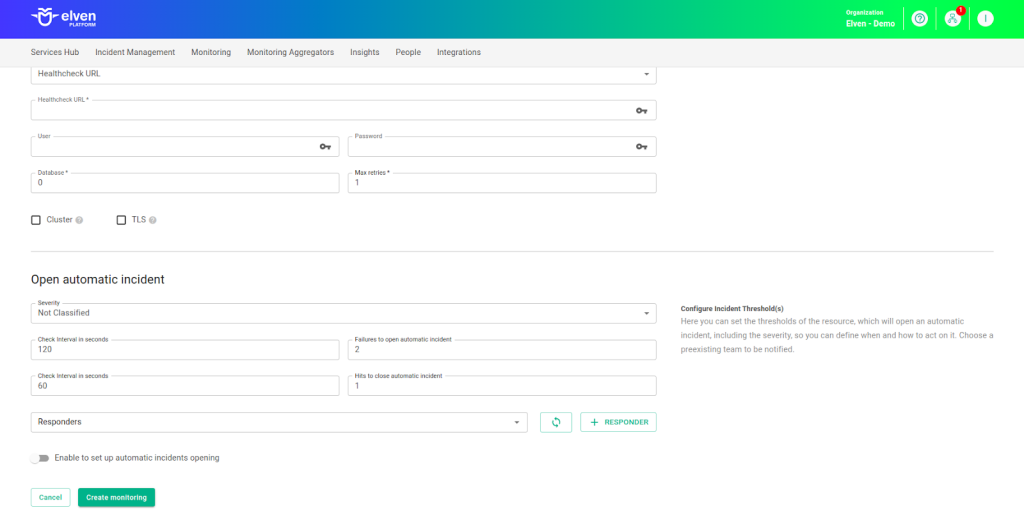
Automatic Incident Opening
You can configure automatic incident opening to ensure a quick response to critical issues. To begin, define the incident severity, allowing you to prioritize according to urgency. Next, adjust the Check Interval, specifying the check frequency in seconds to continuously monitor the resource. This helps ensure you're always one step ahead, detecting problems as soon as they arise.
Additionally, select the team to be notified whenever an incident occurs and enable the "Enable to set up automatic incidents opening" option to ensure the configuration is active. With this setup, the platform automates incident management, making the response process faster and more efficient, without the need for manual intervention. This ensures your team is always ready to resolve any issue with speed and precision.
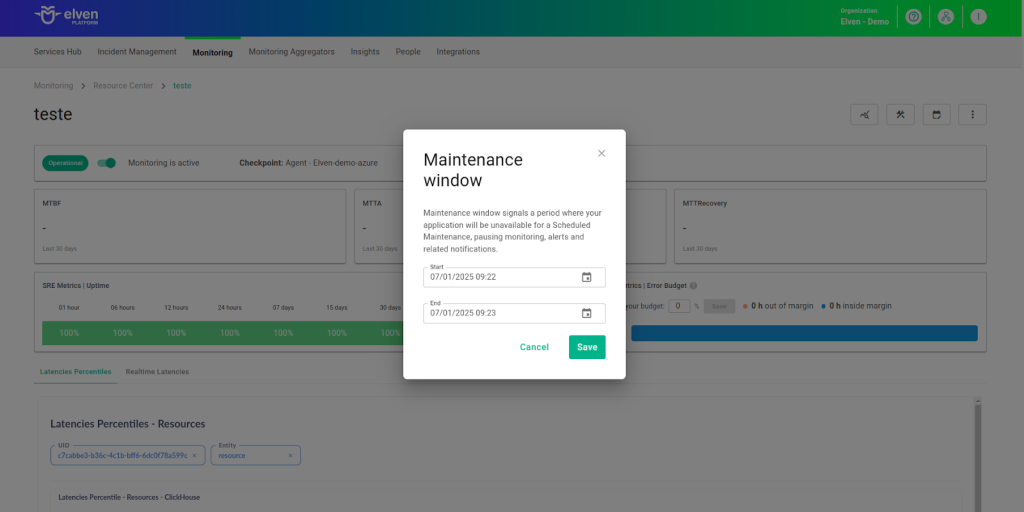
Maintenance Window
We also have the Maintenance Window, an essential feature for managing planned maintenance periods in your application. During this time, checks are temporarily paused, preventing monitoring, alerts, and notifications from being triggered while you perform updates or adjustments. This allows maintenance to proceed smoothly, without generating unnecessary notifications or false alarms, ensuring your operations continue in an orderly manner without unexpected interruptions in performance reports.
For example, imagine you need to update the payment system of an e-commerce platform, making backend adjustments such as installing new security certificates. To do this, you can configure a Maintenance Window for a specific time, such as 12/13/2024, from 2:00 PM to 2:30 PM. During this period, the Elven Platform suspends checks, preventing the monitoring system from logging temporary failures or triggering false alerts. This way, you can make the necessary changes calmly, knowing that the monitoring system will not be affected during maintenance.
This approach ensures that the update is carried out in an organized manner, without affecting the user experience or generating unwanted notifications.
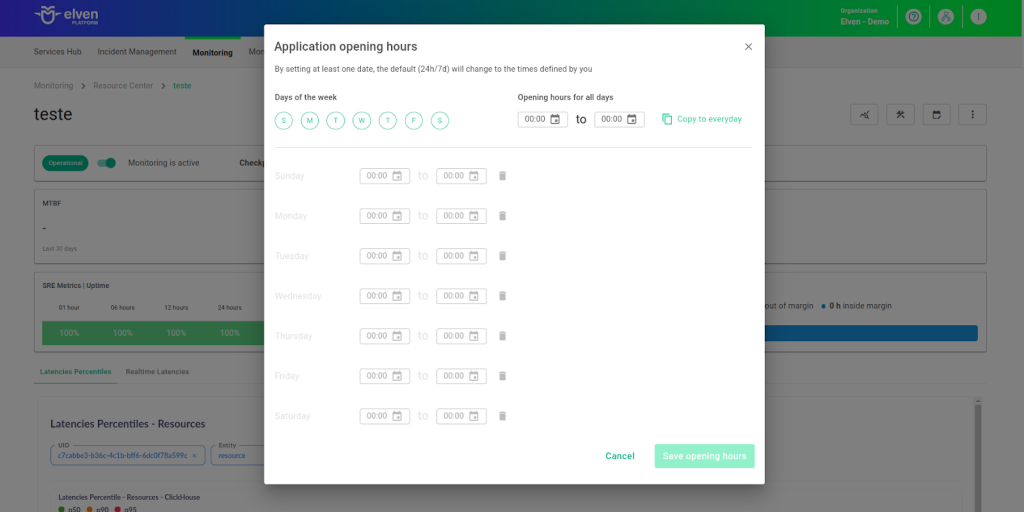
Application Opening Hours
You can also rely on the Application Opening Hours feature, which allows you to configure your application's operating hours. This functionality is essential for customizing monitoring based on the periods when your application is actually active, avoiding alerts and notifications outside of business hours. This makes monitoring more aligned with your business’s real needs, ensuring more accurate reports and efficient management.
For example, imagine your application operates only from Monday to Friday, between 9:00 AM and 6:00 PM. You can configure Application Opening Hours to reflect this schedule by specifying the days and operating periods. With this setup, the Elven Platform automatically disables checks outside these hours, preventing the logging of failures that don’t affect end users and avoiding unnecessary alerts.
This approach optimizes performance analysis, focusing only on relevant periods and providing a clearer view of your application’s health during its operational hours.
Glossary of Technical Terms
Redis: An open-source in-memory data store used as a database, cache, and message queue. With support for advanced data structures, it offers high performance, low latency, and configurable persistence. Scalable and distributed, it is ideal for applications that require fast operations, and is widely used for caching, session management, and real-time counting. Compatible with various programming languages, it is an efficient solution for optimizing the performance of modern systems.
Interval: The time interval between automatic checks performed during monitoring.
Timeout: The maximum time allowed for the monitoring system to receive a response from the monitored resource before registering a failure.
Checkpoint Cloud: The location of the monitoring agent, which can be a preexisting environment or one created by the user.
Host: The URL address of the monitored resource. If an IP address is required, it must be stored in a Secret for enhanced security.
Secret: A resource used to store sensitive information, such as IP addresses or credentials, ensuring security and organization.
Database: Refers to the Redis database number to be monitored. Redis allows multiple databases within the same instance, identified by numbers (starting from 0). A value of “0” indicates the default database is being used.
Max retries: Defines the maximum number of reconnection attempts to Redis in case of a communication failure. A value of “1” means only one additional attempt will be made.
Cluster: An option that, when enabled, indicates that Redis is operating in cluster mode. Redis Cluster allows data to be distributed across multiple instances for greater scalability and availability.
TLS: Indicates whether communication with Redis will use TLS (Transport Layer Security). This configuration ensures that data exchanged between the Redis client and server is encrypted, increasing security.
Enable to set up automatic incidents opening: An option that, when enabled, activates automatic incident creation upon detection of critical issues.
Severity: The level of criticality assigned to an incident, allowing it to be prioritized based on urgency.
Check Interval: The time interval, in seconds, for performing continuous checks on the monitored resource.
Maintenance Window: A feature that temporarily pauses monitoring, alerts, and notifications during planned maintenance periods.
Application Opening Hours: A configuration that defines the operating hours of the application, aligning monitoring with active periods and avoiding alerts outside those hours.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

